Effective from 1 January 2021
The following Standards is effective for accounting periods beginning on or after 1 January 2021. It may be possible to apply these changes early depending on local legislation and the requirements of the particular change in concern.
Interest Rate Benchmark Reform Phase 2 (Amendments to IFRS 9, IAS 39, IFRS 7, IFRS 4 and IFRS 16)
In September 2020, the IASB published Interest Rate Benchmark Reform Phase 2 (Amendments to IFRS 9, IAS 39, IFRS 7, IFRS 4 and IFRS 16), finalising its response to the ongoing reform of interest rate benchmarks around the world. The amendments aim to assist reporting entities to provide investors with useful information about the effects of the reform on their financial statements.
Many interbank offer rates (IBORs) are expected to be replaced by new benchmark Risk-Free Rates (RFRs) in future reporting periods. This has resulted is the IASB needing to address potential financial reporting implications after the reform of an interest rate benchmark. The IASB has completed this project in two stages, the first one focussing on providing relief for hedging relationships which was finalised in September 2019 by publishing Interest Rate Benchmark Reform (Amendments to IFRS 9, IAS 39 and IFRS 7). This second set of amendments focus on issues arising post replacement, ie, when the existing interest rate benchmark is actually replaced with alternative benchmark rates.
The amendments
The main amendments can be summarized as follows:
| Issue | Proposal |
| Highly probable requirement and prospective assessments of hedge effectiveness |
Where an entity currently designates IBOR cash flows, the replacement of IBORs with new interest rate benchmarks raises questions over whether it will be possible to make the assertion that those cash flows will still occur in a hedge of highly probable future cash flows, and whether the hedging relationship meets the requirements to be viewed as effective on a prospective basis? The IASB therefore has provided exceptions for determining whether a forecast transaction is highly probable or whether it’s no longer expected to occur. Specifically, the amendments state that an entity should apply those requirements assuming that the interest rate benchmark on which the hedged cash flows are based is not altered as a result of interest rate benchmark reform. It also includes exceptions to the hedge accounting requirements in IFRS 9 and IAS 39 so that an entity assumes that the interest rate benchmark on which the hedged cash flows are based, and/or the interest rate benchmark on which the cash flows of the hedging instrument are based, are not altered as a result of interest rate benchmark reform when the entity determines whether: - there is an economic relationship between the hedged item and the hedging instrument applying IFRS 9 - or the hedge is expected to be highly effective in achieving offsetting by applying IAS 39. |
| Designating a component of an item as the hedged item |
The changes amend the hedge accounting requirements in IFRS 9 and IAS 39 for hedges of the benchmark component of interest rate risk that are not contractually specified and that are affected by interest rate benchmark reform. Specifically, it states that an entity applies the requirement (that the designated risk component or designated portion is separately identifiable) only at the inception of the hedging relationship. There is one exception to this, and that is when an entity frequently resets a hedging relationship because both the hedging instruments and the hedged item frequently change, the entity applies the requirement only when it initially designates a hedged item in that hedging relationship. |
Effective date and transition
The amendments are effective for annual periods beginning on or after 1 January 2021, with earlier application permitted.
They should be applied retrospectively, and restatement of prior periods is not required, however entities can restate prior periods, if it is possible without the use of hindsight.
Commercial significance
Few number of entity affected - The amendments affect entities with hedging relationships directly affected by IBORs.
Medium impact on affected entities - These amendments provide urgent relief from the effects of IBOR on hedge accounting. Using these amendments, we believe it should be possible for most reporting entities to transition from IBOR benchmarks to alternative benchmarks without hedge discontinuation which would be a useful outcome for users of financial statements.
Effective from 1 January 2022
In May 2020 the IASB issued a collection of narrow scope amendments to IFRS Standards. The collection includes amendments to three Standards as well as Annual Improvements to IFRS Standards, which addresses non-urgent (but necessary) minor amendments to four standards.
- References to the Conceptual Framework (Amendments to IFRS 3)
- Proceeds before Intended Use (Amendments to IAS 16)
- Onerous Contracts – Cost of Fulfilling a Contract (Amendments to IAS 37)
- Annual Improvements to IFRS Standards 2018-2020 Cycle (Amendments to IFRS 1, IFRS 9, IFRS 16, IAS 41)
The amendments
| Standard affected | Subject | IASB's summary of amendment |
|
IFRS 3 ‘Business Combinations’ |
References to the Conceptual Framework |
Adds a new exception to the recognition principle in order to make sure that the accounting remains unchanged. |
|
IAS 16 ‘Property, Plant and Equipment’ |
Proceeds before Intended Use |
Prohibits an entity from deducting from the cost of property, plant and equipment amounts received from selling items produced while the company is preparing the asset for its intended use. Instead, an entity will recognise such sales proceeds and related cost in profit or loss. |
|
IAS 37 ‘Provisions, Contingent Liabilities and Contingent Assets’ |
Onerous Contracts – Cost of Fulfilling a Contract |
Specifies which costs an entity includes when assessing whether a contract will be loss-making. |
Annual Improvements to IFRS Standards 2018-2020 Cycle
| Standard affected | Subject | IASB's summary of amendment |
|
IFRS 1 ‘First time Adoption of International Financial Reporting Standards’ |
Subsidiary as a First-time Adopter |
Simplifies the application of IFRS 1 by a subsidiary that becomes a first time adopter after its parent in relation to the measurement of cumulative translation differences. |
|
IFRS 9 ‘Financial Instruments’ |
Fees in the ‘10 per cent’ Test for De-recognition of Financial Liabilities |
Clarifies the fees an entity includes when assessing whether the terms of a new or modified financial liability are substantially different from the terms of the original financial liability. |
|
Illustrative Examples Accompanying IFRS 16 ‘Leases’ |
Lease Incentives |
Removes potential for confusion regarding lease incentives. |
|
IAS 41 ‘Agriculture’ |
Taxation in Fair Value Measurements |
Removes a requirement to exclude cash flows from taxation when measuring fair value thereby aligning the fair value measurement requirements in IAS 41 with those in other IFRS Standards. |
Commercial significance
Few number of entity affected - The amendments make changes to relatively narrow areas within IFRS.
Low impact on affected entities - The amendments and the IASB’s Annual Improvements process addresses non-urgent, but necessary minor amendments to IFRS. By their nature then, their commercial significance can be expected to be low. Overall the changes are uncontroversial.
Effective date of new standards
(based on Standards issued at 31 December 2020)
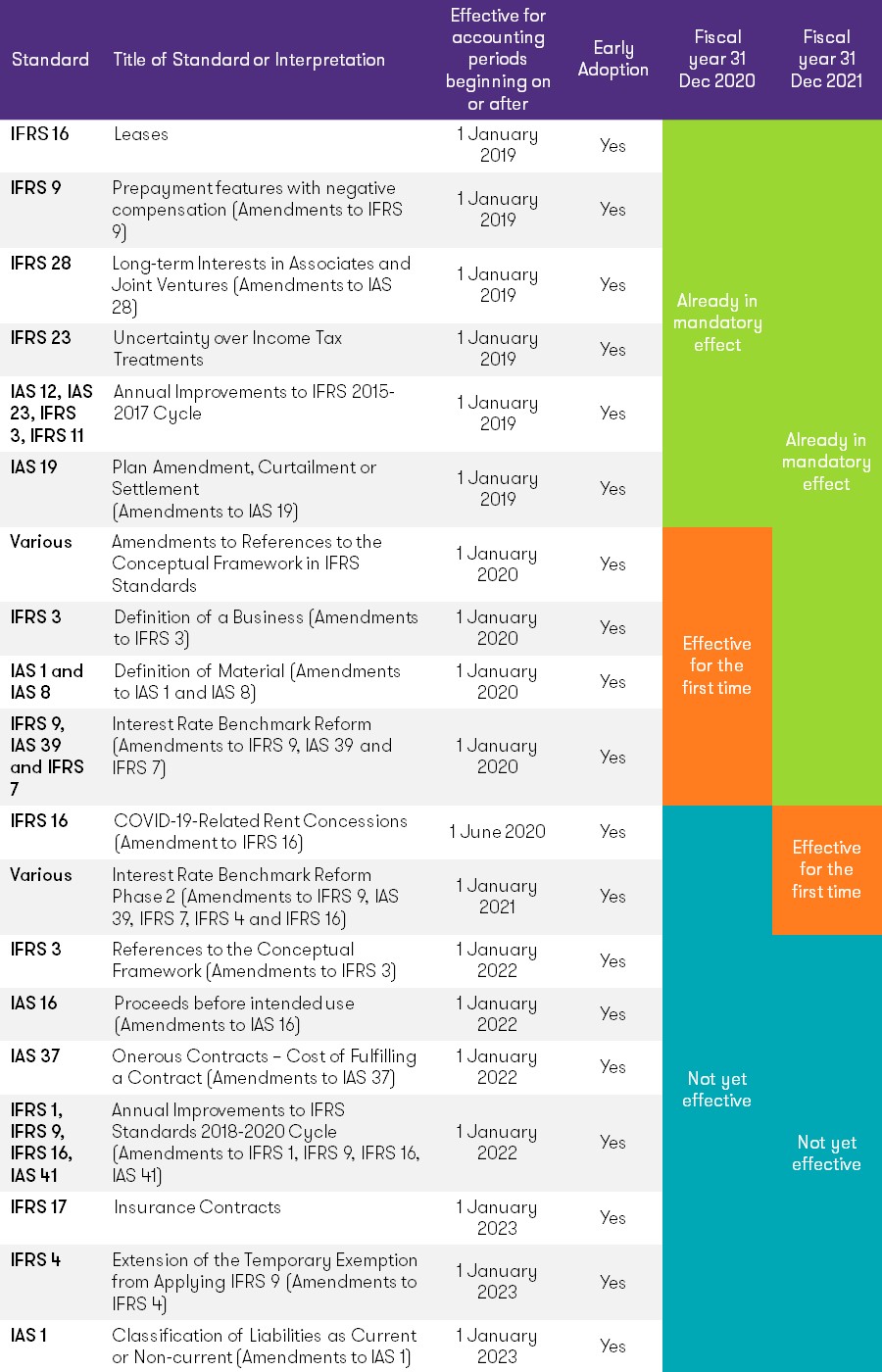
Our full publication on “Navigating the changes to International Financial Reporting Standards – 2021 Edition”
This newsletter highlights key changes in IFRS with effective dates on 1 January 2021 and 2022.
For full information of changes in IFRS applicable for fiscal year ends 31 March 2020, 30 June 2020, 30 September 2020, 31 December 2020 and 31 December 2021 and information on IFRS changes from 1 January 2023, please read our full report in English at the following link:



